The SPAC parade continues in this shortened week with news that community social network Nextdoor will go public via a blank-check company. The unicorn will merge with Khosla Ventures Acquisition Co. II, taking itself public and raising capital at the same time.
Per the former startup, the transaction with the Khosla-affiliated SPAC will generate gross proceeds of around $686 million, inclusive of a $270 million private investment in public equity, or PIPE, which is being funded by a collection of capital pools, some prior Nextdoor investors (including Tiger), Nextdoor CEO Sarah Friar and Khosla Ventures itself.
Notably, Khosla is not a listed investor in the company per Crunchbase or PitchBook, indicating that even SPACs formed by venture capital firms can hunt for deals outside their parent’s portfolio.
Per a Nextdoor release, the transaction will value the company at a “pro forma equity [valuation] of approximately $4.3 billion.” That’s a great price for the firm that was most recently valued at $2.17 billion in a late 2019-era Series H worth $170 million, per PitchBook data. Those funds were invested at a flat $2 billion pre-money valuation.
So, what will public investors get the chance to buy into at the new, higher price? To answer that we’ll have to turn to the company’s SPAC investor deck.
Our general observations are that while Nextdoor’s SPAC deck does have some regular annoyances, it offers a clear-eyed look at the company’s financial performance both in historical terms and in terms of what it might accomplish in the future. Our usual mockery of SPAC charts mostly doesn’t apply. Let’s begin.
Nextdoor’s SPAC pitch
We’ll proceed through the deck in its original slide order to better understand the company’s argument for its value today, as well as its future worth.
The company kicks off with a note that it has 27 million weekly active users (neighbors, in its own parlance), and claims users in around one in three U.S. households. The argument, then, is that Nextdoor has scale.
A few slides later, Nextdoor details its mission: “To cultivate a kinder world where everyone has a neighborhood they can rely on.” While accounts like @BestOfNextdoor might make this mission statement as coherent as ExxonMobil saying that its core purpose was, say, atmospheric carbon reduction, we have to take it seriously. The company wants to bring people together. It can’t control what they do from there, as we’ve all seen. But the fact that rude people on Nextdoor is a meme stems from the same scale that the company was just crowing about.
Underscoring its active user counts are Nextdoor’s retention figures. Here’s how it describes that metric:
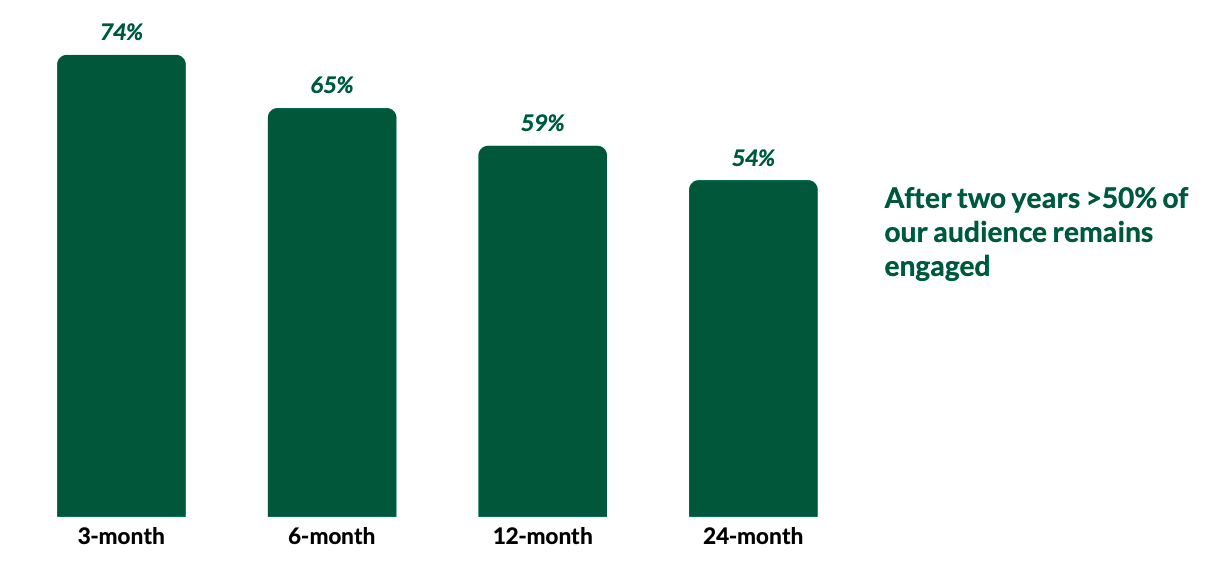
Image Credits: Nextdoor SPAC investor deck
These are monthly active users, mind, not weekly active, the figure that the company cited up top. So, the metrics are looser here. And the company is counting users as active if they have “started a session or opened a content email over the trailing 30 days.” How conservative is that metric? We’ll leave that for you to decide.
The company’s argument for its value continues in the following slide, with Nextdoor noting that users become more active as more people use the service in a neighborhood. This feels obvious, though it is nice, we suppose, to see the company codify our expectations in data.
Nextdoor then argues that its user base is distinct from that of other social networks and that its users are about as active as those on Twitter, albeit less active than on the major U.S. social networks (Facebook, Snap, Instagram).
Why go through the exercise of sorting Nextdoor into a cabal of social networks? Well, here’s why:
